The Model Context Protocol (MCP) architecture is a system designed to facilitate communication between MCP Hosts (such as Claude Desktop, IDE, and AI Tools) and various data sources including local filesystems, databases, and the internet.
The overview presents a step-by-step guide to building a custom MCP (Model Context Protocol) Server using Python, detailing the MCP architecture where MCP Clients interact with an MCP.
The MCP (Model Context Protocol) workflow showcases how various AI models and agents, including OpenAI, Claude, Deepseek, CrewAI, LangChain, LangGraph, CopilotKit, and Llamaindex, interact with the MCP.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) architecture overview illustrates how MCP Clients within Agent A and Agent B (MCP HOSTs) communicate with multiple MCP Servers (A, B, C, Y, Z) using the MCP Protocol. It highlights secure collaboration, task and state
The MCP Server architecture within the Model Context Protocol depicts how MCP Clients from an MCP HOST interact with the MCP Server to access local data sources (e.g., files, APIs, remote services) and remote services via APIs. The MCP Server acts as a central hub, facilitating communication and data exchange between multiple MCP Clients and diverse data environments.
The AI Model Training Process within the Model Context Protocol presents a five-step workflow:
Each step is visually connected in a circular flow, emphasizing the iterative nature of the process, with icons representing key activities like data handling, technique selection, training execution, validation checks, and testing evaluations.
The process of building AI tools with remote MCP (Model Context Protocol) using Azure Functions features an Azure Function App that hosts MCP Tools. MCP Clients, including VS Code & Copilot and MCP Inspector, connect via SSE (Server-Sent Events) and webhooks to the Azure Function App, which provides functionalities like getting code snippets from a collection, saving code snippets to a collection, and managing MCP tool registry and tool metadata.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) powers AI through its role in AI integration, with an API-centric hub connecting to five key areas: External Search Engines for dynamic information retrieval, Internal Knowledge Bases for context-aware searching, Database Querying for accurate data access, Secure Plugins for controlled interactions with external tools, and Enhanced Productivity for boosting AI-assisted workflows and automations.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) process is outlined through a six-step workflow depicted in a spiral design: 1) Identify MCP Server, 2) Publish Metadata, 3) Browse Tools, 4) Understand Requirements, 5) Authenticate Securely, and 6) Invoke Functionality. Each step is visually represented with icons, guiding users through the process of engaging with MCP servers, from server identification to executing desired functions.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) integration compares the pre-MCP “NxM Problem,” where AI models (GPT-4, Claude, Gemini, Llama) connect to data sources (Google Drive, Slack, GitHub, Postgres, Custom APIs) with complex, non-standardized integrations, to the streamlined “Universal Protocol” approach with MCP. MCP, likened to a “USB-C port for AI,” offers a standardized protocol, bidirectional flow, tool discovery, and built-in security, connecting models to diverse data sources like APIs, files, and more with ease.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) and Function Calling approaches for processing a user query about the weather in San Francisco are compared. In the MCP process, the user query is sent to an MCP Client within an MCP HOST, which, after API request approval, chooses a weather tool via the MCPServer, queries the Weather API, and outputs the result (18 degrees Celsius) through an LLM. In contrast, Function Calling involves the user query being processed by a Function Call application, which uses a large language model to interpret the prompt and function declaration, queries the Weather API directly, and returns the same result.
The MCP Server architecture within the Model Context Protocol showcases how MCP Clients from an MCP HOST interact with the central MCP Server to access both Local Data Sources (e.g., files, APIs, remote services) and Remote Services via APIs. The design highlights a streamlined connection between multiple MCP Clients and diverse data environments, emphasizing the server’s role as a hub for efficient data exchange.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) ecosystem details its key components and their interactions within a unified framework. It highlights the MCP Client, which connects AI hosts like Claude and ChatGPT to the MCP Server, facilitating data retrieval from diverse sources such as files, databases, and APIs. The design emphasizes the protocol’s role in standardizing communication, with a focus on tool discovery, resource management, and secure data exchange.
Risus sit amet ornare suscipit, orci lorem sollicitudin justo vel congue metus quam ac mi. Nulla euismod magna et luctus condimentum.
Quisque a cursus nibh. Nunc commodo, massa in faucibus lacinia, orci orci dictum risus, at rutrum orci lectus vitae felis.
The infographic highlights how AI integration with the Model Context Protocol (MCP) enhances AI capabilities through five key aspects:

Maecenas porta ante eget lectus maximus eleifend. Sed ut viverra diam, a tempus sem. Sed nec metus urna.

Risus sit amet ornare suscipit, orci lorem sollicitudin justo vel congue metus quam ac mi.
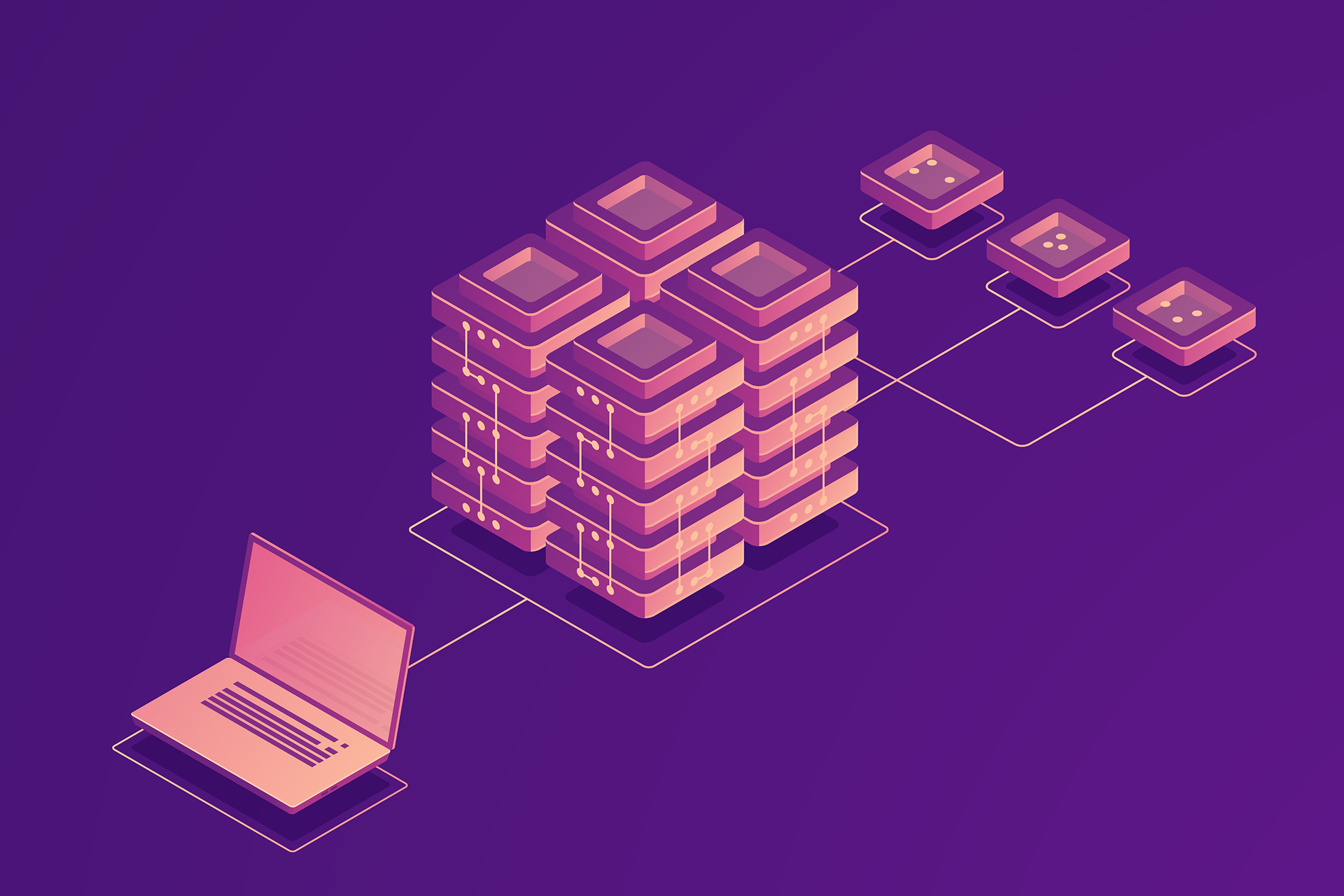

The Model Context Protocol (MCP) architecture illustrates how MCP Clients embedded in AI hosts like Claude and ChatGPT communicate with the MCP Server to access a variety of data sources, including files, databases, and APIs. It emphasizes the protocol’s role in enabling seamless data exchange through standardized communication, featuring components such as tool discovery, resource management, and secure interactions.
Bert Blevins is a recognized cybersecurity expert who specializes in Privileged Access Management (PAM), identity and access management (IAM), and cybersecurity best practices.





